OTC Pain Relievers: What Works, What Risks, and What You Need to Know
When you reach for an OTC pain reliever, over-the-counter medications used to reduce pain, fever, or inflammation without a prescription. Also known as non-prescription analgesics, these drugs are among the most taken medicines in the world—yet most people don’t know how they truly affect their body. Whether it’s a headache, sore back, or menstrual cramps, you grab something from the cabinet without thinking. But OTC pain relievers aren’t harmless snacks. They can quietly damage your stomach, kidneys, or heart if used the wrong way.
Two main types dominate the shelf: NSAIDs, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that reduce both pain and inflammation. Also known as anti-inflammatories, they include common names like ibuprofen and naproxen. And then there’s acetaminophen, a pain and fever reducer that doesn’t fight inflammation. Also known as paracetamol, it’s the go-to for people avoiding stomach issues—but it’s far more dangerous to the liver than most realize. These aren’t interchangeable. NSAIDs can worsen heart failure or raise blood pressure. Acetaminophen can cause sudden liver failure if you take too much, especially with alcohol or certain meds. Both can quietly harm you over time, even if you feel fine.
People with chronic pain often use these daily without checking in with a doctor. But studies show that long-term NSAID use increases hospitalization risk by up to 40% in people with heart conditions. Meanwhile, acetaminophen overdose is the #1 cause of acute liver failure in the U.S.—and many cases happen because people don’t realize it’s in their cold medicine, sleep aids, or combo pills. You’re not just taking one thing. You’re stacking risks.
That’s why this collection dives into real-world problems: how NSAIDs affect heart failure, why seniors need safer options like Actifen, how opioid painkillers lead to constipation, and what alternatives actually work. You’ll find clear comparisons, hidden dangers, and practical steps to use these meds without putting your health at risk. No fluff. No marketing. Just what you need to know before the next pill goes down.
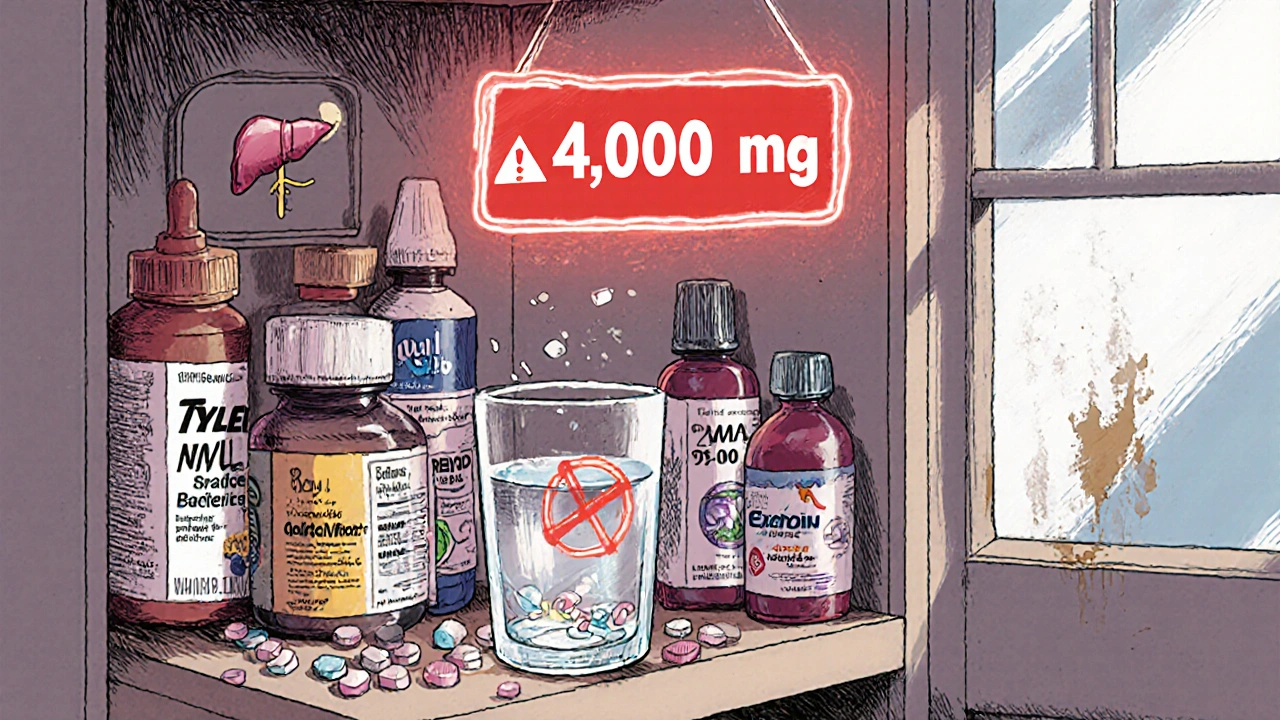
How to Avoid Liver Injury from OTC Pain Relievers
- Laura Ledas
- Nov, 18 2025
Acetaminophen is the leading cause of acute liver failure in the U.S., often from unintentional overdoses. Learn how to safely use OTC pain relievers, spot hidden acetaminophen, and protect your liver-especially if you have liver disease or drink alcohol.
Learn More