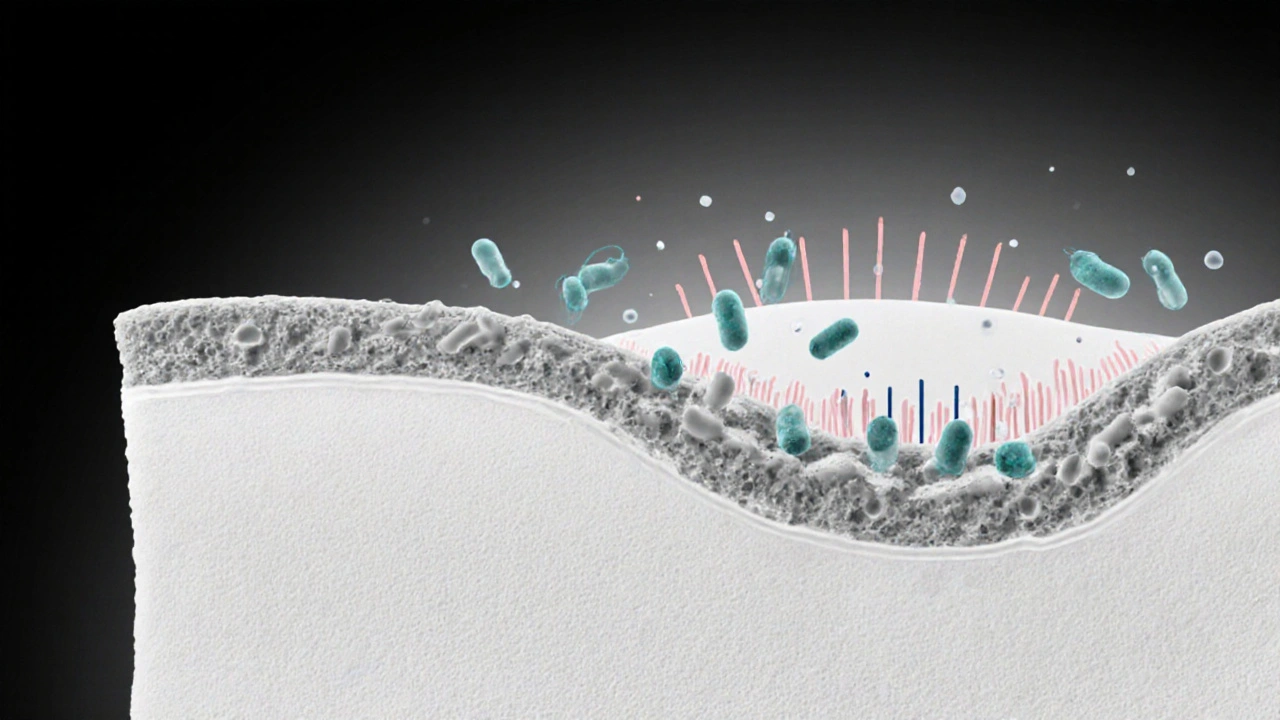
Innate Immunity – Your Body’s First Line of Defense
When talking about Innate immunity, the body’s rapid, non‑specific defense that reacts within minutes to any foreign threat. Also known as non‑specific immunity, it relies on built‑in sensors called pattern recognition receptors, molecules that spot common features of microbes and trigger an immediate response. These receptors sit on cells like macrophages and neutrophils, ready to flag invaders the moment they appear. The moment a pathogen is recognized, a cascade of signals fires, leading to inflammation, fever, and the recruitment of more immune cells. In short, innate immunity sets the stage for everything that follows, buying your body precious time while the more specialized adaptive system gears up.
Core Components and Their Connections
Beyond receptors, the innate system includes phagocytosis, the process where immune cells engulf and destroy microbes. Think of it as the cellular vacuum cleaner that clears out bacteria, viruses, and debris. While phagocytes work, they release chemicals that cause inflammation, the redness, heat, and swelling you feel during infection or injury. Inflammation isn’t just a side effect; it’s a vital signal that attracts more immune troops and helps seal off damaged tissue. Meanwhile, adaptive immunity, the slower, highly specific response that creates memory cells for future protection watches the scene, learns the enemy’s details, and later mounts a precise attack. The two systems are intertwined: innate signals guide adaptive activation, and adaptive antibodies can boost innate functions. This partnership means that a well‑functioning innate system reduces the workload for adaptive immunity, keeping overall inflammation balanced and preventing chronic disease.
Why does all this matter to you? Because many health topics you’ll explore below—autoimmune therapies like dimethyl fumarate, hormone‑related skin issues, drug‑induced immune changes—hinge on how innate immunity behaves. A drug that calms an over‑active innate response can ease autoimmune flare‑ups, while a medication that unintentionally triggers innate receptors might cause unwanted inflammation. Understanding the basics helps you read those articles with confidence, spot why a medication works, and recognize when lifestyle choices (like diet or stress management) can support your body’s first line of defense. Innate immunity is more than a science term; it’s a daily player in infection risk, vaccine response, and even recovery from injury. Below you’ll find practical guides, safety tips, and the latest research that tie back to these core immune concepts. Dive in and see how the first responders in your body shape the health topics you care about.
How the Immune System Prevents and Fights Vaginal Infections
- Laura Ledas
- Aug, 22 2025
Learn how the immune system protects the vagina, why infections happen, and practical steps to strengthen your natural defenses.
Learn More