Caffeine and ADHD: How Stimulants Affect Focus, Sleep, and Medication
When you have ADHD, a neurodevelopmental condition marked by difficulty with attention, impulse control, and executive function. Also known as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, it often leads people to seek out stimulants—whether prescription or not—to feel more alert and focused. That’s where caffeine, a natural stimulant found in coffee, tea, and energy drinks that blocks adenosine receptors in the brain. It’s the most widely consumed psychoactive substance in the world. comes in. Many people with ADHD wonder: does caffeine help? Does it hurt? Can it replace medication? The answer isn’t simple, but it’s practical.
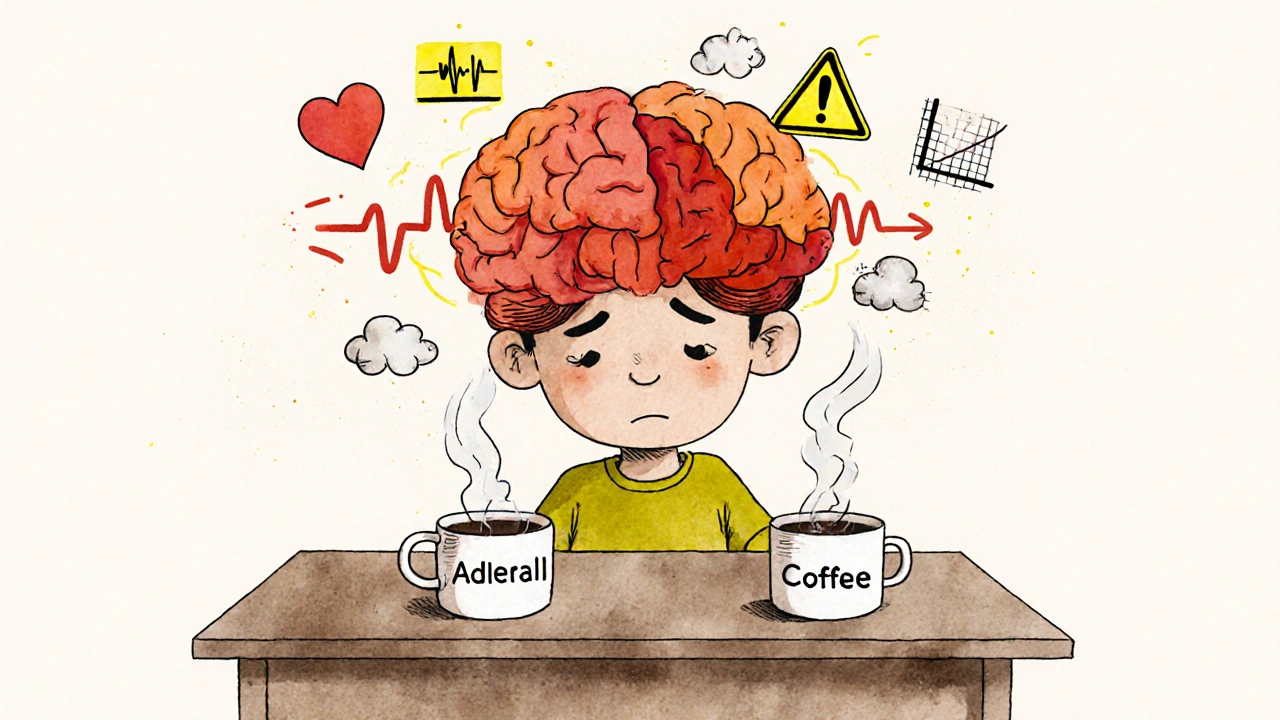
Some studies show caffeine can improve attention and reduce impulsivity in people with ADHD, especially at low to moderate doses. It works similarly to prescription stimulants like methylphenidate or amphetamines by boosting dopamine and norepinephrine—chemicals that are often low in ADHD brains. But unlike Adderall or Vyvanse, caffeine doesn’t come with a precise dosing chart or medical oversight. One cup might help you focus; three might leave you jittery, anxious, or unable to sleep. And sleep? That’s the big problem. People with ADHD already struggle with insomnia. Caffeine can make it worse, especially if taken after noon. Poor sleep then makes ADHD symptoms worse the next day—a cycle that’s hard to break.
Then there’s the issue of ADHD medication interactions, how caffeine affects the way prescription stimulants are processed in the body. Caffeine can slow down how quickly your liver breaks down some ADHD drugs, leading to higher blood levels and stronger side effects. That means more racing heart, more anxiety, more trouble sleeping. If you’re on methylphenidate or amphetamine-based meds, mixing them with caffeine isn’t just common—it’s risky without monitoring. And if you’re on non-stimulant meds like atomoxetine or guanfacine, caffeine might still push your blood pressure too high.
Real people with ADHD report mixed results. Some swear by their morning black coffee as a low-cost, low-side-effect boost. Others say caffeine made their anxiety unbearable or turned their nights into sleepless chaos. The key isn’t whether caffeine is good or bad—it’s whether it works for you, at your dose, with your meds, and your sleep habits. That’s why this collection of articles dives into real-world experiences, scientific findings, and practical tips. You’ll find guides on timing caffeine around meds, managing side effects, spotting when it’s doing more harm than good, and what alternatives actually work. No fluff. Just what helps—and what doesn’t—when you’re trying to manage ADHD with or without drugs.
Caffeine and ADHD Medications: Synergy and Side Effect Risks
- Laura Ledas
- Nov, 14 2025
Mixing caffeine with ADHD meds like Adderall can boost focus-but it also raises heart rate, anxiety, and crash risks. Learn how to safely manage this common combo with science-backed tips.
Learn More